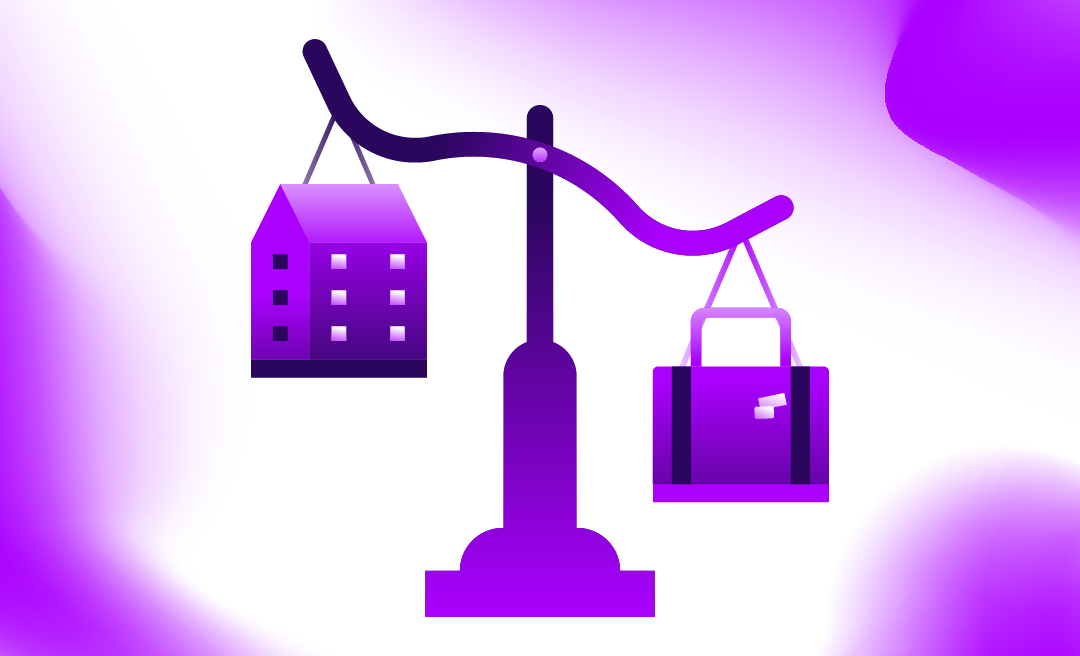
Soft skills are 85% of a person’s success in a profession
Business analyst Viktor Kublanov shares a list of key soft skills that every IT specialist should have, and suggests sources you can use to learn more about them.
.jpeg)
The Wearecommunity.io platform raised an important topic for the development of an IT specialist — upgrading soft skills. We’ve included some of the main points below.
Soft skills — highly personal, non-technical skills that help us handle our daily tasks and work with people. We need to develop and grow this skill set regardless of our work specialization. Soft skills are valuable in all areas of life and work; they are sometimes thought of as personality traits, and are related to emotional intelligence.
Hard skills — professional skills needed for specific tasks in daily work. They are based on technical knowledge or training. Hard skills can readily be learned and their effectiveness can be measured.
Research from Harvard University, the Stanford Research Center, and the Carnegie Foundation suggests that “soft skills” account for 85% of a person’s professional success, while hard skills account for only 15%.
Google’s Project Aristotle involved an internal investigation to determine the most productive teams within the company. It provided unexpected results, and Google discovered that its best teams were mixed groups of employees with strong soft skills, including such important skills as communication, empathy, and leadership.
The top 14 essential soft skills, and sources that you can use to learn more about them.
1. Communication. An information transfer process, an exchange of knowledge or information between people. Communication helps us build interpersonal relationships and resolve personal and professional issues.
Books:
- Morten Hansen "Collaboration: How Leaders Avoid the Traps, Build Common Ground, and Reap Big Results";
- Mark Rhodes "How To Talk To Absolutely Anyone: Confident Communication for Work, Life and Relationships"’;
- Jim Camp "Start with NO…The Negotiating Tools that the Pros Don’t Want You to Know";
- Roger Fisher, William L. Ury, Bruce Patton "Getting to Yes: Negotiating Agreement Without Giving In".
2. Critical thinking. The ability to manage information in a balanced way. We live in an intensive flow of information every day. It’s easy to lose focus. This skill helps us: verify and clarify all necessary information, clearly understand the connections between different facts, think rationally, make the right decisions, and formulate strong arguments. Without critical thinking you can easily become a victim of manipulation.
Books:
- Diane F. Halpern "Thought and Knowledge: An Introduction to Critical Thinking";
- Vincent Ruggiero "Art of Thinking, The: A Guide to Critical and Creative Thought";
- Erik Vance "Suggestible You: The Curious Science of Your Brain’s Ability to Deceive, Transform, and Heal";
- Tom Chatfield "Critical Thinking: Your Guide to Effective Argument, Successful Analysis and Independent Study".
3. Customer focus. The ability to identify the needs and desires of your audience. This skill helps you connect customers’ expectations and needs with your project goals. Enhancing this skill also requires efforts to increase listening skills, as actively listening to customer feedback and concerns can significantly improve your understanding and responsiveness to their requirements.
Books:
- Jack Mitchell "Hug Your Customers: The Proven Way to Personalize Sales and Achieve Astounding Results";
- Carl Sewell, Paul B. Brown "Customers for Life: How to Turn That One-Time Buyer Into a Lifetime Customer";
- Ken Blanchard, Sheldon Bowles "Raving Fans : Revolutionary Approach to Customer Service";
- Philip Graves "Consumerology: The Truth about Consumers and the Psychology of Shopping".
4. Project Management. A project involves different people: the customer, contractors, assistants, third-party entities. The project manager stands at the center of the system. They manage and control the life cycle of the project and are responsible for its success.
Books:
- Mark Forster "Do It Tomorrow and Other Secrets of Time Management";
- Jeff Sutherland, J.J. Sutherland "Scrum: The Art of Doing Twice the Work in Half the Time";
- David J. Anderson, Donald G Reinertsen "Kanban: Successful Evolutionary Change for Your Technology Business";
- Tom DeMarco, Tim Lister "Peopleware: Productive Projects and Teams".
5. Mentoring. The basic professional knowledge of a junior employee may be different from what is required for day-to-day work tasks. A more experienced mentor typically shares their knowledge and skills to assist the professional growth and adaptation of the less experienced employee.
Books:
- John C. Maxwell "Mentoring 101: What Every Leader Needs to Know";
- Hilarie Owen "The Complete Guide to Mentoring: How to Design, Implement and Evaluate Effective Mentoring Programmes".
6. Nonviolent Communication. This is a subset of communication skills generally, it involves a method of communicating clearly and accurately, and getting your point across by first creating empathy between the parties to the discussion. In Nonviolent Communication, you communicate with the goal of establishing interpersonal harmony, gathering facts then expressing your needs and formulating a request. This skill helps to negotiate mutually acceptable solutions in meetings and in personal communication with colleagues and loved ones.
Books:
- Marshall B. Rosenberg "Nonviolent Communication: A Language of Life: Life-Changing Tools for Healthy Relationships (Nonviolent Communication Guides)";
- Patrick King "Improve Your People Skils: Build and Manage Relationships, Communicate Effectively, Understand Others, and Become the Ultimate People Person".
7. Decision-making. The ability to consciously choose the best solution from among possible options. This skill involves making informed decisions after you have assessed the relevant information; it is key to achieving goals quickly and maximizing benefits.
Books:
- Chip Heath, Dan Heath "Decisive: How to Make Better Choices in Life and Work";
- Dr. Adam Ferner "Think Differently: Open your mind. Philosophy for Modern Life";
- Tal Ben-Shahar "Choose the Life You Want: The Mindful Way to Happiness".
8. Problem-solving. This skill helps you solve challenges at work and in life. It generally involves multiple steps, including observation, analysis, and implementation. The more you practice it, the more difficult situations you’ll be able to handle and resolve. Problem-solving is similar to project management and decision-making — you overcome challenges to achieve goals and get results.
Books:
- Daniel Kahneman "Thinking, Fast and Slow";
- Morgan D. Jones "The Thinker’s Toolkit: 14 Powerful Techniques for Problem Solving";
- Nat Greene "Stop Guessing: The 9 Behaviors of Great Problem Solvers".
Course:
9. Emotional intelligence. The ability to understand and manage your own emotions, and to recognize and influence the emotions of others. This skill helps you solve practical problems, make decisions, and build communication with others.
Books:
- Daniel Goleman "Emotional Intelligence: Why It Can Matter More Than IQ" and "Working With Emotional Intelligence";
- Anthony Mersino "Emotional Intelligence for Project Managers: The People Skills You Need to Achieve Outstanding Results";
- Susan David "Emotional Agility";
- Travis Bradberry, Jean Greaves "Emotional Intelligence 2.0".
Course:
10. Knowledge management. Knowledge management helps you choose sources of information, sort them, analyze the available information, and achieve the objectives of your organization by optimally applying the knowledge you’ve gained.
Books:
- Josh Kaufman "The Personal MBA 10th Anniversary Edition";
- Kay Peterson, David A. Kolb "How You Learn Is How You Live: Using Nine Ways of Learning to Transform Your Life";
- Dan Waldschmidt "Edgy Conversations: How Ordinary People Achieve Outrageous Success".
11. Working with uncertainty. Successfully working with uncertainty allows you to quickly respond to changing requirements, make optimal decisions with incomplete information, and leverage available resources.
Books:
- Tim Harford "Messy: The Power of Disorder to Transform Our Lives";
- Neen James "Attention Pays: How to Drive Profitability, Productivity, and Accountability";
- Carl Honore "In Praise of Slowness: Challenging the Cult of Speed";
- Paul Woods "How to Do Great Work Without Being an Asshole";
- Annie Duke "Thinking in Bets: Making Smarter Decisions When You Don’t Have All the Facts".
12. Lean manufacturing. The ability to eliminate waste, find bottlenecks, and improve the process of creating something. This skill helps to optimize resources for a particular person or an entire production. It is necessary for entrepreneurs who are involved in small, medium, or large-scale production.
Books:
- James P. Womack, Daniel T. Jones "Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation";
- Thomas Fabrizio, Don Tapping "5S for the Office: Organizing the Workplace to Eliminate Waste";
- Shigeo Shingo, Andrew P. Dillon "A Study of the Toyota Production System (Produce What Is Needed, When It’s Needed)";
- Michael L. George "Lean Six Sigma: Combining Six Sigma Quality with Lean Production Speed".
13. Ecological thinking. The ability to deal with events without causing harm to oneself or others. Ecological thinking recognizes the interconnectedness of individuals and systems and involves accepting responsibility for one’s actions and employing a positive attitude toward the world. The skill helps you to be passionate about what you do and derive satisfaction from the results of your work.
Books:
- John G. Miller "Flipping the Switch: Unleash the Power of Personal Accountability Using the QBQ!";
- Joshua Becker "The More of Less: Finding the Life You Want Under Everything You Own";
- Yutaka Yazawa "How to Live Japanese";
- Timothy Morton "Being Ecological".
14. Self-reflection. An ability to analyze one’s actions, emotions, and thought processes. It helps you evaluate your actions, and has been shown to improve performance. This skill helps you make better decisions using your knowledge of yourself and awareness of your needs.
Books:
Do you want to know what skills you possess, what web developer soft skills you need to further develop, and — most importantly — what IT profession best suits your collection of skills and abilities? Take the psychology and neuroscience test on the Anywhere Club website.
.png)
