The Power of Machine Learning: How Is It Used in CRM Systems?
The author of this article is EPAM Lead Functional Consultant Vitaly Malyshev.
CRM and CRM systems
We deal with CRM systems almost every day without even noticing it. Have you called a barbershop or other business and been greeted by name? Have you earned bonus points for purchasing a new phone? Have you ever added items to the shopping cart of an online store and forgotten about them, but then received a reminder? Or maybe when buying a coloring book, you’ve been offered the option to also purchase colored pencils?
If you’ve had any of these experiences, most likely there is a CRM system behind it. CRM (customer relationship management) is a technology-driven solution that enables organizations to understand their customers' needs and behaviors to build stronger relationships.
CRM systems offer a lot of benefits for business, ranging from efficient data management to personalized customer interactions. Companies use CRM systems to streamline their sales processes, automate marketing campaigns, and provide exceptional customer service. The centralization of customer data enables a comprehensive view of complex customer interactions. It helps businesses tailor their strategies to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
CRM systems examples
Several CRM systems have become industry standards, aiding businesses across diverse sectors. Examples include:
SAP CX has extensive integration capabilities with all kinds of SAP solutions and its own implementation methodology.
Salesforce offers a cloud-based platform, known for its versatility and scalability.
Microsoft Dynamics CRM seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft applications, offering a comprehensive solution.
HubSpot provides an all-in-one inbound marketing platform that includes CRM.
Zoho CRM caters to businesses of all sizes with its user-friendly interface.

Machine learning and its use in CRM
A subset of artificial intelligence, machine learning (ML), is a powerful tool for optimizing and automating various processes.
I would like to emphasize that AI is the broader concept of creating intelligent machines, while ML is a specific approach within AI that focuses on training machines to learn from data. ML enables systems to improve their performance on specific tasks through experience and data analysis.
Machine learning is already widely used in many areas of our lives, and CRM is no exception. In the context of CRM, ML plays an important role in transforming data into actionable insights that help businesses make informed decisions.
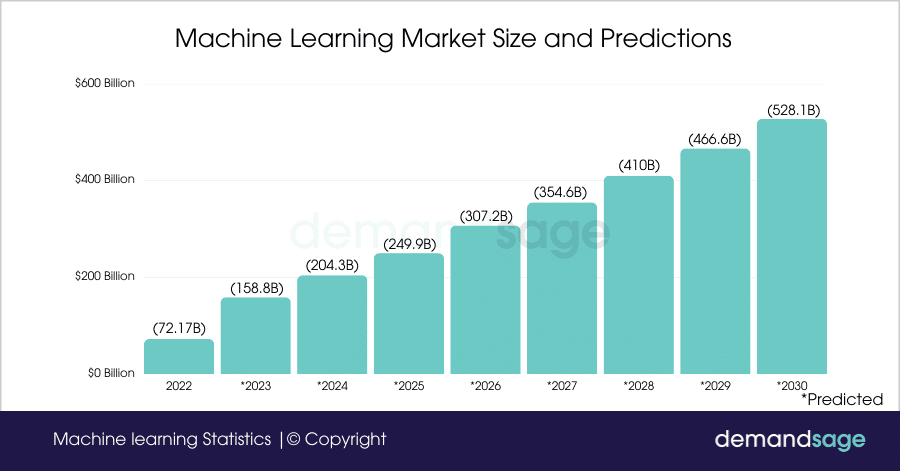
ML involves the development of algorithms that enable computers to learn and make predictions or decisions without explicit programming. These algorithms use patterns and insights derived from data, continually improving as more data becomes available. In the case of CRM, ML facilitates the extraction of valuable insights from the vast amounts of customer data generated.
One of the notable applications of ML in CRM is predictive analytics. By analyzing historical data, ML algorithms can predict future customer behaviors, preferences, and trends.
The use of machine learning benefits both the business and the customer:
ML helps companies focus their efforts on the most promising activities and frees employees from routine tasks. And, of course, it enables companies to make more sales and generate more revenue.
The customer, in turn, receives genuinely useful recommendations and spends less time solving problems.
Examples of using ML in CRM systems
Below, I briefly mention scenarios that machine learning already covers using SAP products (Cloud for Sales and Cloud for Service) as an example.
Sales scenarios
Here are 3 main sales scenarios:
Scoring for leads and opportunities: ML is used to predict whether a lead/opportunity can be won or lost. In the web-interface, specialists can observe the ML-calculated score of the lead/opportunity and the key factors on which the calculation was based.
Business text intelligence: natural language understanding (NLU) is used to obtain actionable insights, such as visits and appointments, from text analysis using business text intelligence. It can, for example, automatically create an appointment in the calendar based on a customer's email.
Product recommendation: ML suggests selling additional products based on what is already in the order. If you are going to buy a new phone, for example, it can suggest buying the appropriate case as well.
Service scenarios
Service scenarios are less visible to you and me as customers, but often they are the most important for solving our issues. For businesses, these scenarios are crucial to stay on good terms with customers and to continue the relationship:
Ticket processing (ticket = customer issue): machine learning is used to automate the ticket categorization and prioritization processes. ML can also find similar past tickets to check for solutions that may apply to the current ticket, calculate time to completion, and recommend the most suitable e-mail response template.
Ticket NLP classification: natural language processing (NLP) can identify ticket language, sentiment, and can extract product and customer identification.
Machine translation and text summarization: NLP can perform auto-translation to the language the user needs and create a summary to save time.
Conclusion
Modern CRM systems are a great example of the evolution of customer relationship management. The integration of machine learning in CRM systems enables businesses to stay ahead in a competitive market by leveraging the power of data-driven insights. As companies prioritize customer-centric strategies, the combination of CRM and machine learning becomes a solution that drives enhanced customer engagement and operational efficiency.
.png)
